The Importance of Advanced Communications Technologies and Services (ACTS): The European Connection
ACTS is an acronym for Advanced Communications Technologies and Services, a programme under the European Community 4th Framework R &TD Programme (collaborative research and technology development in Europe). ACTS is one of the biggest European R&TD investments with around 120 projects in place. The DTI/EPSRC High Performance Interfaces & Protocols (HPIP) LINK programme is the complementary UK initiative. In the words of the Commissions overview:
"ACTS is part of a new agenda - outlined in the European Union's White Paper on 'Growth, Competitiveness and Employment' - aimed at making direct contribution to Europe's economic and social development. ACTS will provide the framework for advanced research and development in the communications field.
ACTS will build on previous European Union R&D programmes, including RACE in telecommunications, giving the impetus for the implementation of the telecommunications needs of the information society.
The work in the ACTS framework will stimulate the development of Integrated Broadband Communications (IBC) in Europe, with all manner of communications - voice and sound, still pictures and video images, data and text - providing boundless opportunities for new users, services and employment. The IBC network will link fixed and mobile communications in a seamless web. Isolated 'islands' of IBC technology are already operating. The challenge is to ensure that widespread IBC services are made available as soon as possible. Everyone, everywhere in the Union should have access to a pan-European IBC network by the turn of the century."
With the development of pan-European IBC as a primary goal, ACTS projects necessarily include a cross section of network service providers (typically the major PTTs), equipment manufacturers (such as Alcatel), telecommunications experts and applications software developers supported by university researchers. Projects work in six main areas of advanced communications (known as the ACTS domains):
- Interactive digital multimedia services
- Photonic Techniques
- High Speed Networking
- Mobility and personal communications networks
- Intelligence in networks and service engineering
- Quality, security and safety of communications services and systems
The Domains of immediate interest to the E-Lib community are Interactive Digital Multimedia services and High Speed Networking - for reasons described below.
A full description of the ACTS Programme and of each project is available in the ACTS '95 Report, available from DG XIII, Directorate B, ACTS Central Office,
Tel. + 32 2 296 34 15,
Fax. + 32 2 295 06 54,
email: ACO@postman.dg13.cec.be;
and on the World Wide Web: http://www.uk.infowin.org/
or
http://www.ispo.cec.be
Further information relevant to ACTS, and other programmes within the European Communities 4th Framework can be found on the UK National Host Office Web server at: http://www.ja.net/UKNationalHost/welcome.html
ACTS & The Research & Library Communities
In simple terms ACTS is coming from the bottom up - focusing on the issues of deploying an Integrated Broadband Communications (IBC) infrastructure, whereas the Telematics & IT (Esprit) programmes within the 4th Framework (FP4) are driven from the user community downwards. Nevertheless ACTS has distinguished itself from its predecessor (RACE) in its concern for user centred trials in applications areas capable of exploitation. These will be of interest to the Library community for a number of reasons.
(1) Broadband Applications - The future of telecommunications
ACTS projects will establish the impact of broadband (a real superhighway) on sought after applications such as information brokerage (eg GAIA, OSM projects), teletraining & distance learning (eg RENAISSANCE, LEVERAGE), public information services (eg KIMSAC) and services to the home (eg MUSIST, AMUSE).
The local testbeds ('Broadband Islands'), National Host services and trans-European broadband connections made available within the programme provide a unique opportunity to forsee the potential and the issues relating to a future 'Superhighway' made up of heterogeneous technologies such as ATM, Cable (CATV) and ISDN connected to local services (both to LANS and the home).
(2) Interactive Multimedia - The future of document delivery
The ACTS programme is specifically focused on multimedia services involving the delivery of interactive audio-visual (AV) 'streams' such as realtime video, music and virtual worlds. This represents a facet of 'next generation' on-demand document delivery services that is typically outside the experience of programmes such as E-Lib, JTAP & FP4 Telematics. ACTS research in this area is closely linked to the emergent DAVIC & TINA-C standards arising from the telecommunications and broadcast sectors as well as equivalent approaches in the Internet community.
(3) Information Brokerage - The future of libraries
In the 2nd Call (1996) the programme has contracted a number of projects in Information Brokerage. These will be investigating aspects of the Search, Locate, Request, Delivery cycle pertinent to the E-Lib Document delivery projects (such as EDDIS & Infobike) and to the MODELS framework. The ACTS programme is particularly concerned with the development of standards in this area which address the necessarily heterogeneous nature of a global network of service suppliers, brokers and clients - as opposed to the development of end-to-end branded supply models. It is notable that the GAIA project will be including standards and experiences from the library domain in this work.
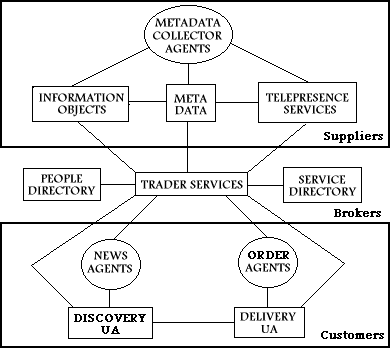
(4) Recognition of Libraries
The ACTS programme has set up a substantial 'horizontal' concertation mechanism to draw together 'Chains' of expertise across projects on key issues. Some of these chains may produce insights of general value for developers of wide area services. It is notable that the General Applications Cultural (GAC) chain will focus on implementation issues in Museums and Libraries.
Furthermore the recent call for ideas for ACTS 2000 (the 5th Framework) included recognition that libraries may evolve into a rich area for broadband service deployment. There is clearly much to be gained by all parties if the library and the ACTS communities can synchronise their ideas, their needs and their dreams through the current programme. The best starting place from a library viewpoint may be those ACTS projects such as GAIA that deal with the generic architectures for the digital supply chain.
Fretwell-Downing lead the GAIA project.
